ROME — The Vatican on Tuesday answered critics and justified its pursuit of an extended agreement with China on bishop nominations, acknowledging difficulties but insisting the effort had achieved limited, positive results.
The Holy See articulated its position on the eve of a visit by U.S. Secretary of State Mike Pompeo, who this month wrote a harsh critique of the Vatican’s 2018 accord with China. Pompeo is scheduled to headline a religious liberty conference on Wednesday with the Vatican secretary of state and foreign minister, two architects of the deal.
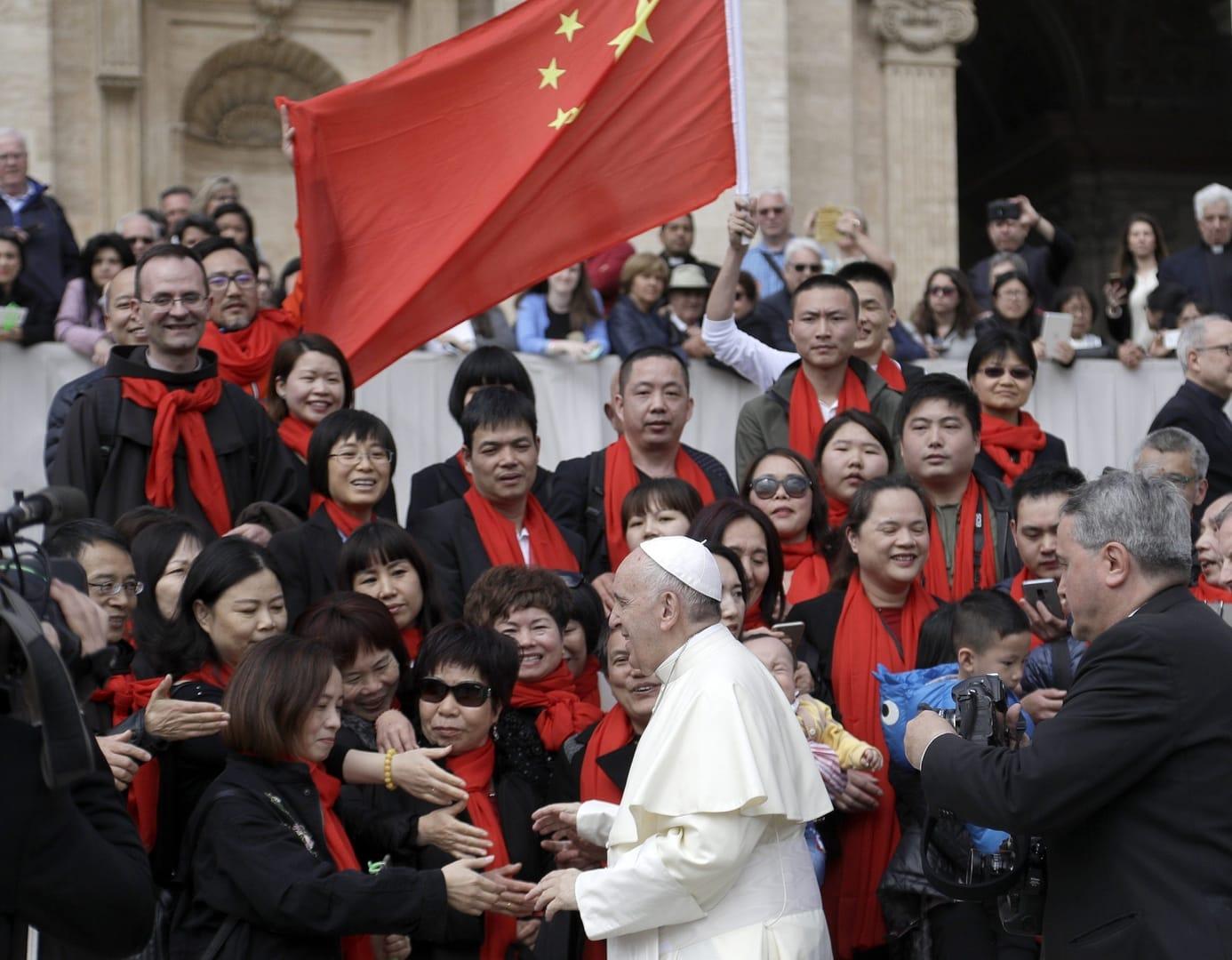
The 2018 accord was aimed at uniting the Catholic flock in China, which is divided between an official church recognized and regulated by the Beijing government, and an underground church that has been loyal to Rome. The agreement included a process for nominating new bishops, regularizing the status of seven bishops who weren’t recognized by Rome and thawing decades of estrangement between China and the Vatican.
Critics of the accord, including the retired archbishop of Hong Kong, some underground faithful in China and conservative Catholics elsewhere, accused the Vatican of betraying the Catholics in China who for decades refused to join the state-sanctioned church.
The critics say the deal also has emboldened the Beijing government in its harsh crackdown on Christians, Muslims, Buddhists and other believers.
Pompeo criticized the accord in an essay published in the conservative Catholic magazine First Things, echoing the Trump administration’s overall criticism of Beijing that has grown amid the coronavirus pandemic in an election year.
“Two years on, it’s clear that the Sino-Vatican agreement has not shielded Catholics from the (Communist) Party’s depredations, to say nothing of the Party’s horrific treatment of Christians, Tibetan Buddhists, Falun Gong devotees and other believers,” Pompeo wrote.
Noting that the deal is up for renewal when it expires next month, Pompeo wrote: “Now more than ever, the Chinese people need the Vatican’s moral witness and authority in support of China’s religious believers.”
In its first official response to such criticism, Vatican editorial director Andrea Tornielli recalled that the accord only covers bishop nominations, and did not enter into political or diplomatic relations with China.
“The Provisional Agreement exclusively treats the process for the appointment of bishops: An essential question for the life of the Church and for the necessary communion between the pastors of the Chinese Catholic Church with the Bishop of Rome and with the bishops throughout the world,” he wrote.
Tornielli quoted the Vatican secretary of state, Cardinal Pietro Parolin, as saying it was worth negotiating an extension to the deal despite “difficulties” aggravated by the virus outbreak.
“Even though contact was blocked in recent months due to the pandemic, the results have been positive, although limited, and suggest going forward with the application of the agreement for another determined period of time,” he said.