LEICESTER, United Kingdom – Fiji is free from British rule, but the Pacific nation still has the “colonial form of power” and is not yet democratic, according to the country’s archbishop.
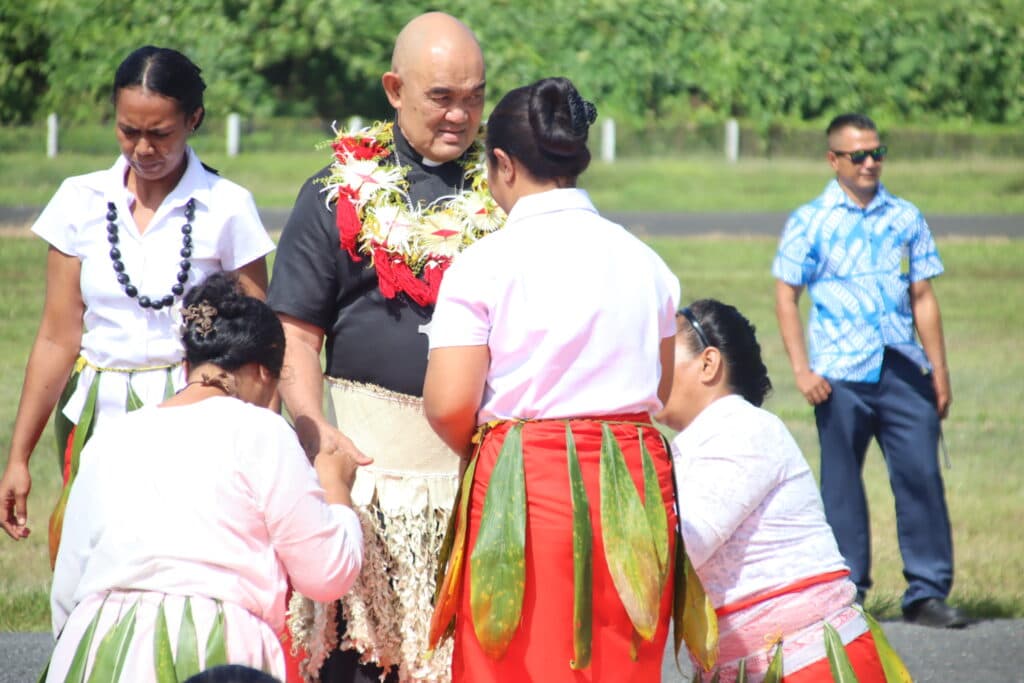
The Republic of Fiji is an island country in the South Pacific Ocean, and has a population of nearly a million people, with approximately 83,000 Catholics.
Archbishop Peter Loy Chong of the capital Suva issued a statement for the Catholics on Oct. 8 to marking the anniversary of the country’s independence from Britain on Oct. 10, 1970.
The population of Fiji is mostly made up of native Fijians, who make up over half the people, and Indo-Fijians descended from contract laborers brought to the islands from India by the British colonial powers in the 19th century. Over the past decade, the Indo-Fijian population has gotten smaller due to emigration, which many say is caused by policies favoring the native Fijian peoples.
“This year, Fiji celebrates 54th Anniversary of independence from British colonial rule,” Loy Chong’s statement says.
“What is British colonial rule? What is the form of power: The British Colonial administration used the ‘indirect rule policy,’ the native rule policy to rule over natives. Through the indirect rule policy, the colonial government incorporated the customary chiefs into the colonial administration,” the archbishop explains.
He said political literature names this form of power as “patron-client” politics.
“Fiji Independence Day should therefore mark, not only the end of British rule but also patron-client politics and a move toward genuine independence,” Loy Chong continues.
“When Fiji became independent in 1970, the colonial administration had already introduced patron-client politics to the Fijian people. Under the patron-client political framework, the chiefs, the military, senior military officers, and sometimes the Church became the clients of the ruling government,” he says.

“We are independent from British rule but we still carry on the colonial form of power and hence, we are not democratic,” the archbishop says.
He also claims that today, globalization is a new form of colonialism.
“A thread that runs through all globalization discourses is increasing connectivity. The boom of information and communication technologies (ICT) forms part of the infrastructure of globalization in finance, capital mobility and export-oriented business activity, transnational communication, migration, travel, and civil society interactions,” he explains.
“Through globalization, the world has become so intensely interconnected in its actions that local boundaries have broken down. Globalization created a homogeneous culture. Increasingly, what happens economically, politically, and socially in a country will significantly influence other countries and their citizens. People, money, and products move around the world with ease, intensity, and at a high velocity, bringing dramatic cultural changes,” Loy Chong adds.
He also claims that with globalization, the multinational corporations and companies “are the new colonists who have power over nation states.”
The Catholic leader says under globalization, the World Bank and IMF are the superpowers controlling economics and politics throughout the world.
“They have taken over the sovereign authority that countries have traditionally held over their nation, by breaking national, cultural, and geographic boundaries. In fact, many governments are forced to serve the multinational corporations rather than the people that elected them,” he says.
The main economic powers in Fiji are tourism, agriculture and fisheries. There are fears that climate change and global trade policies will hurt the people in the small island nation.
In his statement, Cong said the free market is the root metaphor for economic globalization.
“Companies demand for full and free control over resources, production, and trade. Therefore, nations have to give corporations’ freedoms in marketing and trade. This means eliminating laws that would in any way hinder the economic activities of corporations. Unfortunately, in many cases this means relaxing laws that protect human dignity, nature, the environment, and the community as a whole,” he says.
“Corporations demand total freedom for their economic activities, so much so that they displace the government in terms of decision-making and setting policies for development,” the archbishop adds, noting some companies even enjoy tax free zone packages.
He also claims the characteristic of globalization in Fiji is the power of multinational corporations over the government. He said global corporations are powerful and do not recognize any borders.
“This is especially true for Third World countries like Fiji that do not have the resources to stand autonomously in terms of economic development. They become easy victims for economic domination by multinational corporations,” Loy Chong says.
“To respond to the negative impacts of globalization, the Catholic Social Teaching upholds two principles for genuine democracy, participation and subsidiarity,” he continues.
He said Pope Paul VI identified participation and equality as fundamental foundations of human dignity and freedom, and taught that there is a basic drive in human beings as they seek greater development, that is, to share responsibility in decision making that shape their individual and collective future.
The archbishop claims globalization suffers from a “democratic deficit.”
He says globalization has two fault-lines in decision making: Local communities do not get an adequate hearing; and the divide between the elites and local communities and even entire states lack true participation.
“In sum, the democratic deficit of globalization means that large numbers of world’s peoples do not participate in a meaningful way in decisions that will directly bear on their well-being,” Loy Chong says.
The archbishop says the principle of subsidiarity calls for local communities to assess, decide, and act at the most local level possible while still being effective in securing the common good.
“The state should take over duties and responsibilities that local communities can carry out themselves. In globalization, nation states have not disappeared, but they now operate within a different context. Nation states retain power, but they must wield that power in collaboration with other powerful nations and multination corporations. In reality, it is the multinational corporations’ that rule the world,” he explains.
He also says Catholic Social Teaching calls for new forms of governance and true political authority, and the creation of new institutions and practices for managing a new world order.
“Globalization – multinational corporation and companies – must be regulated and directed,” the archbishop writes.
Loy Chong says Catholic Church has two key roles in Fiji’s political history: To set forth the requirements of just social action set forth in the Bible and Catholic Social Teaching; and to denounce social, economic, or political actions and structures “in the name of justice and Kingdom of God.”
“The Church wants to build a just society, and it seeks to do so on the solid foundation of four fundamental values: Truth, Freedom, Justice and Love. In its commitment to a just society, the Catholic Church seeks to enhance true democracy in Fiji,” the archbishop writes.
Follow Charles Collins on X: @CharlesinRome