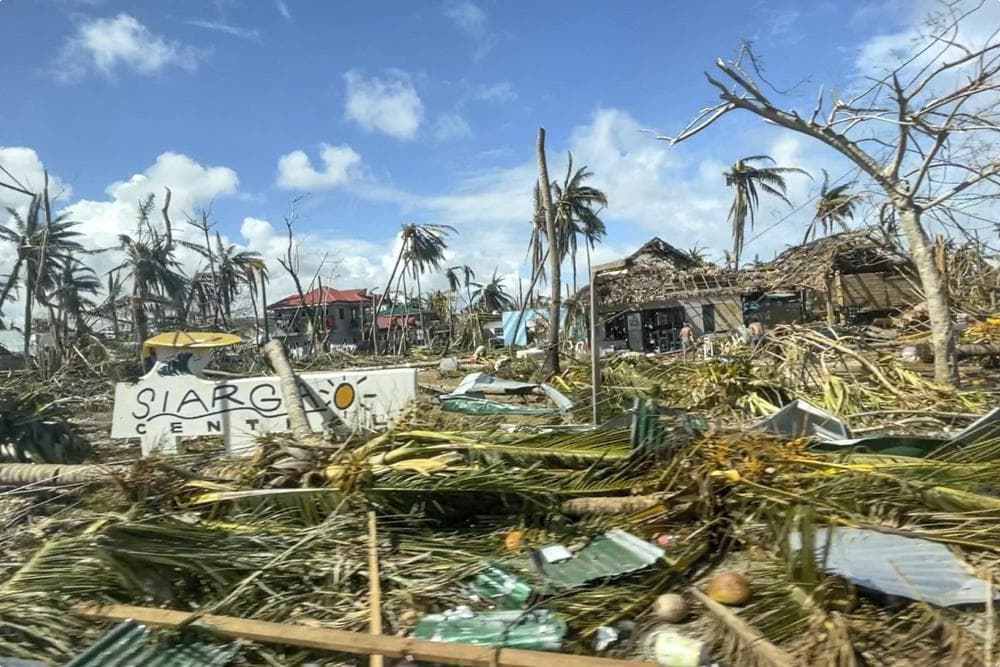
MANILA, Philippines — The death toll following the strongest typhoon to batter the Philippines this year has risen to more than 200, with 52 other people still missing and several central towns and provinces grappling with downed communications and power outages and pleading for food and water, officials said Monday.
At its strongest, the typhoon packed sustained winds of 121 miles per hour and gusts of up to 168 mph before it blew out Friday into the South China Sea.
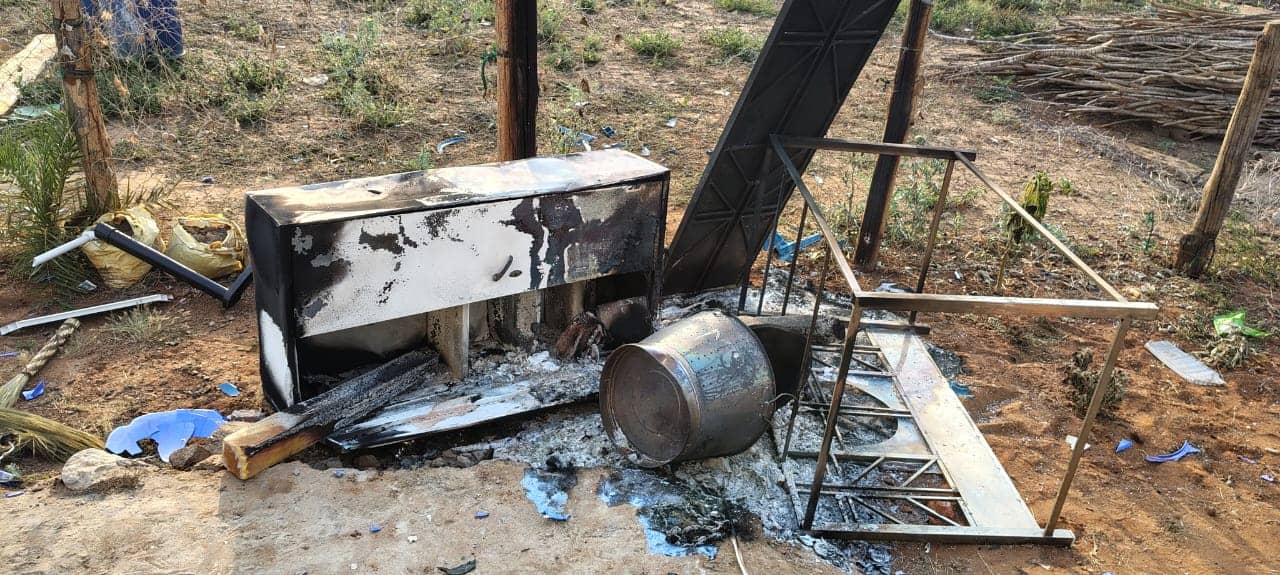
At least 208 people were killed, 52 remained missing and 239 were injured, according to the national police. The toll was expected to increase because several towns and villages remained out of reach due to downed communications and power outages although massive clean-up and repair efforts were underway.
Many died due to falling trees and collapsing walls, flash flood and landslides. A 57-year-old man was found dead hanging from a tree branch and a woman was blown away by the wind and died in Negros Occidental province, police said.
Governor Arlene Bag-ao of Dinagat Islands, among the southeastern provinces first hit by the typhoon, said Rai’s ferocity on her island province of more than 130,000 was worse than that of Typhoon Haiyan, one of the most powerful and deadliest typhoons on record and which devastated the central Philippines in November 2013 but did not inflict any casualties in Dinagat.
“If it was like being in a washing machine before, this time there was like a huge monster that smashed itself everywhere, grabbed anything like trees and tin roofs and then hurled them everywhere,” Bag-ao told The Associated Press by telephone. “The wind was swirling north to south to east and west repeatedly for six hours. Some tin roof sheets were blown away then were tossed back.”
At least 14 villagers died and more than 100 others were injured by flying tin roofs, debris and glass shards and were treated in makeshift surgery rooms in damaged hospitals in Dinagat, Bag-ao said. Many more would have died if thousands of residents had not been evacuated from high-risk villages.
Like several other typhoon-hit provinces, Dinagat remained without electricity and communications and many residents in the province, where the roofs of most houses and buildings were ripped off, needed construction materials, food and water. Bag-ao and other provincial officials traveled to nearby regions that had cellphone signals to seek aid and coordinate recovery efforts with the national government.
More than 700,000 people were lashed by the typhoon in central island provinces, including more than 400,000 who had to be moved to emergency shelters. Thousands of residents were rescued from flooded villages, including in Loboc town in hard-hit Bohol province, where residents were trapped on roofs and trees to escape from rising floodwaters.
Coast guard ships ferried 29 American, British, Canadian, Swiss, Russian, Chinese and other tourists who were stranded on Siargao Island, a popular surfing destination that was devastated by the typhoon, officials said.
Emergency crews were scrambling to restore electricity in 227 cities and towns, officials said. Power has been restored in only 21 areas so far. Cellphone connections in more than 130 cities and towns were cut by the typhoon but at least 106 had been reconnected by Monday, officials said. Two local airports remained closed except for emergency flights, but most others have reopened, the civil aviation agency said.
Bag-ao and other officials were concerned that their provinces may run out of fuel, which was in high demand due to the use of temporary power generators, including those used for refrigerated warehouses with large amounts of coronavirus vaccine stocks. Officials delivered vaccine shipments to many provinces for an intensified immunization campaign, which was postponed last week due to the typhoon.
At the Vatican, Pope Francis expressed his closeness Sunday to the people of the Philippines, referencing the typhoon “that destroyed many homes.”
About 20 storms and typhoons annually batter the Philippines, which lies between the Pacific Ocean and the South China Sea. The Southeast Asian archipelago also lies along the seismically active Pacific “Ring of Fire” region, making it one of the world’s most disaster-prone countries.