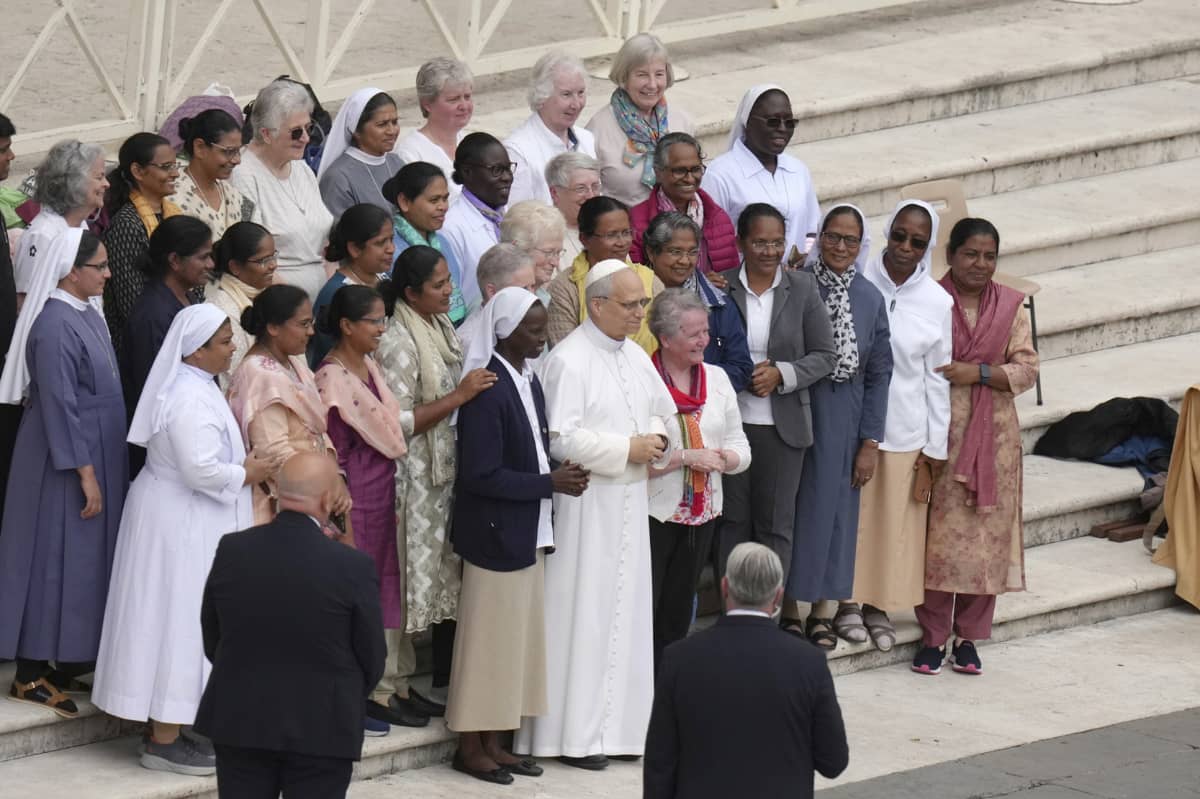
ROME — Interreligious dialogue is an important way to counter fundamentalist groups as well as the unjust accusation that religions sow division, Pope Francis said.
Meeting with members of the Argentine Institute for Interreligious Dialogue Nov. 18, the pope said that in “today’s precarious world, dialogue among religions is not a weakness. It finds its reason for being in the dialogue of God with humanity.”
Recalling a scene from the 11th-century poem, “The Song of Roland,” in which Christians threatened Muslims “to choose between baptism or death,” the pope denounced the fundamentalist mentality which “we cannot accept nor understand and cannot function anymore.”
“We must beware of fundamentalist groups; each (religion) has their own. In Argentina, there are some fundamentalist corners there,” he said. “Fundamentalism is a plague and all religions have some fundamentalist first cousin.”
According to its website, the Institute for Interreligious Dialogue was founded in Buenos Aires in 2002 and was inspired by then-Cardinal Jorge Mario Bergoglio as a way “to promote understanding among men and women of different religious traditions in our city and the world.”
The pope welcomed the members of the institute who are in Rome to reflect on the document on “human fraternity” and improving Christian-Muslim relations, which was signed Feb. 4 by Francis and Sheikh Ahmad el-Tayeb, the grand imam of al-Azhar and a leading religious authority for many Sunni Muslims.
The intention of the document, the pope explained, was a way to adopt a “culture of dialogue” while respecting each other’s unique identity.
“This is key: Identity cannot be negotiated because if you negotiate your identity, there is no dialogue, there is submission. Each (religion) with its own identity is on the path of dialogue,” he said.
The “complex human reality” of brotherhood, the pope continued, can be seen in scripture when God asks Cain about the whereabouts of his brother.
That same question must be asked today and lead members of all religions to reflect on ways of becoming “channels of brotherhood instead of walls of division,” he said.
To see the dangers of fundamentalism, Christians must also reflect on their own history, he said, including the Thirty Years’ War, which began in 1618 as a conflict between Catholic and Protestant states, and the St. Bartholomew’s Day massacre of 1572, which saw the targeted assassinations of Huguenots by Catholic mobs in France.
“A bit of history should frighten us,” the pope said. “Whoever doesn’t feel frightened from within should ask themselves why.”
Francis said he hoped that the document on “human fraternity” would be “welcomed by the international community, for the good of the human family who must pass from simple tolerance to true and peaceful coexistence.”
“It is important to show that we believers are a factor of peace for human societies and in doing so, we will respond to those who unjustly accuse religions of inciting hatred and causing violence,” the pope said.
Crux is dedicated to smart, wired and independent reporting on the Vatican and worldwide Catholic Church. That kind of reporting doesn’t come cheap, and we need your support. You can help Crux by giving a small amount monthly, or with a onetime gift. Please remember, Crux is a for-profit organization, so contributions are not tax-deductible.